Several types of Central Tendency can be defined: The commons are
- The Arithmetic Mean
- The Median
- The Mode
- The Geometric Mean
- The Harmonic Mean
The Arithmetic Mean: - The Arithmetic Mean of a grouped frequency distribution is defined as
A = any guessed or assumed class mark.
f = Frequency of each class interval.
n = Sum of total frequency.
i = Range of class interval.
d = Deviation of the assumed class mark from each class interval by the range of class interval.
d = (Xi – A) / i
The Median: - The Median of a grouped is defined as
Where,
Me = Median of the total class.
fc = Previous cumulative frequency of all classes above the media class.
fm = Frequency of the corresponding class interval.
i = range of class interval.
L = Lower class boundary of median class.
n = Sum of total frequency.
The Mode: - The Mode of a set of number is that value which occurs with the greatest frequency.
The Mode for a grouped data/frequency distribution is denoted by
Where,
L = Lower limit of modal class interval.
∆1 = Difference between modal and pre-modal group.
∆2 = Difference between modal and post-modal group
i = range of class interval.
The Geometric Mean: - The Geometric Mean is for a grouped frequency distribution is denoted by
Where,
G = Geometric Mean
n = sum of total frequency.
fi = Frequency corresponding each class interval.
xi = Class Mark.
The Harmonic Mean: - The Harmonic Mean H for a grouped frequency distribution is
Where,
H = Harmonic Mean.
n = sum of total frequency.
fi = Frequency corresponding each class interval.
xi = Class Mark.
Problem: -
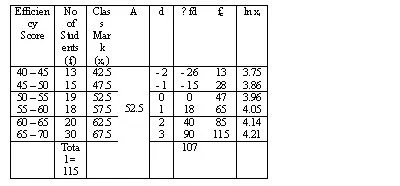
The given frequency is the efficiency score of 115 students in their 70% marks. Find the Arithmetic Mean, Median, Mode, Geometric Mean and Harmonic Mean.
Solution:
Some special measurements following any section of Central Tendency:
- Quartiles
- Deciles and
- Percentile
Quartiles: - The Quartiles are those values in a series which divide the total frequency into four equal parts. It is denoted by Q where
Where,
r = 1, 2, 3,…….
Lr = Lower limit of the Quartiles class,
n = Sum of the total frequency,
r = Position of Quartiles,
Fr = Cumulative frequency of the pre-rth Quartiles class,
fr = Corresponding frequency,
i = Range of class interval.
Deciles: - The Deciles are those values in a series which divide the total frequency into ten equal parts. It is denoted by D where
Where,
r = 1, 2, 3,…….
Lr = Lower limit of the Deciles class,
n = Sum of the total frequency,
r = Position of Deciles,
Fr = Cumulative frequency of the pre-rth Deciles class,
fr = Corresponding frequency,
i = Range of class interval.
Percentiles: - The Percentiles are those values in a series which divide the total frequency into 100 equal parts. It is denoted by P where
Where,
r = 1, 2, 3,…….
Lr = Lower limit of the Percentiles class,
n = Sum of the total frequency,
r = Position of Percentiles,
Fr = Cumulative frequency of the pre-rth Percentiles class,
fr = Corresponding frequency,
i = Range of class interval.












Comments
Post a Comment